


| Pair Name | Vitamin C, Anti-PD-1 antibody | ||
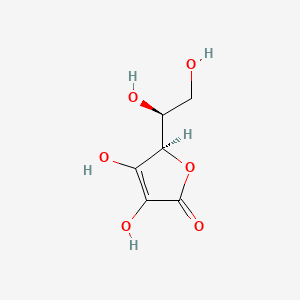
| Phytochemical Name | Vitamin C (PubChem CID: 54670067 ) | ||
| Anticancer drug Name | Anti-PD-1 antibody (PubChem CID: / ) | ||
| Structure of Phytochemical |
|
Download
2D
MOL
3D
MOL
|
|
| Structure of Anticancer Drug |

|
Download
2D
MOL
3D
MOL
|
|
| Pair Name | Vitamin C, Anti-PD-1 antibody | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2B33.5] | Lymphoma | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Inhibition-->Anti-PD1 checkpoint | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | IL12B | hsa3593 |
| Up-regulation | Expression | GZMB | hsa3002 | |
| In Vitro Model | A20 | Reticulum cell sarcoma | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_1940 |
| SU-DHL-6 | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma germinal center B-cell type | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2206 | |
| OCI-Ly1 | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1879 | |
| OCI-Ly7 | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma germinal center B-cell type | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1881 | |
| OCI-Ly3 | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma activated B-cell type | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_8800 | |
| In Vivo Model | 40 BALB/c mice received a subcutaneous (s.c.) right flank injection of 5×10⁶ A20 tumor cells in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and were randomly assigned to 4 groups of 10 mice: vehicle, anti-PD1 (α-PD1), AA, and AA+α-PD1. | |||
| Result | This study shows that AA treatment 1) increases immunogenicity of lymphoma cells; 2) enhances intratumoral infiltration of CD8+ T cells and macrophages; and 3) synergizes with anti-PD1 checkpoint inhibition in a syngeneic lymphoma mouse model via marked activation of cytotoxic cells (cytotoxic T cells and NK cells) and antigen presenting cells. The data provide a compelling rationale for testing combinations of high-dose AA and anti-PD1 agents in patients with aggressive B cell lymphoma and in preclinical models of other malignancies. | |||
| No. | Title | Href |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | High-dose ascorbic acid synergizes with anti-PD1 in a lymphoma mouse model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jan 21;117(3):1666-1677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1908158117. | Click |
